Home / First Semester
Chapter 4: Database Management Systems
The ER data models is based on a perception of real world that consist of a collection of basic objects called entities and relationship among these objects. In ER model a database can be modeled as a collection of entities, and relationship among entities. Overall logical structure of a database can be expressed graphically by E-R diagram.
Different symbols used in ER-Diagram:
2. Diamond: Diamond represents relationship.
3. Oval: The oval or ellipse is used to represent attributes of entities.
4. Line: The oval or ellipse is used to represent attributes of entities.
Components of ER-Database model
- Entity: An entity is a "thing" or "object" in the real world that is different from other objects. An entity has a set of properties and the values for some set of properties may uniquely identify an entity. For example, if student is an entity, is identified by registration number. It is represented by rectangle.
- Attribute: An attribute describes some property or characteristics of the entity. For e.g.: student name, student address, and student age are attributes of the entity student_profile.
- Relationship: A relationship is an association among several entities and represents meaningful dependencies between them. It is represented by diamond.
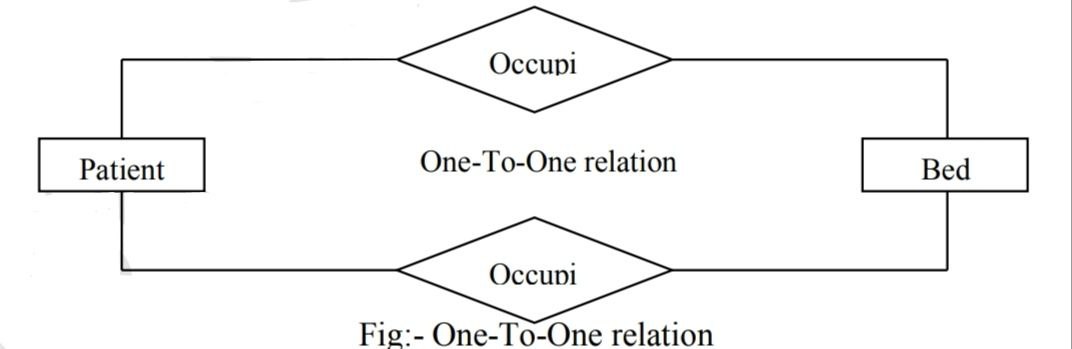
To provide the control and work with multiple fields certain relationship are generated and present with a diagram called the entity relationship diagram. There are three types of relationships between entities. They can be shown in an entity-relation diagram. Also known as E-R diagram. a.) One-To-One
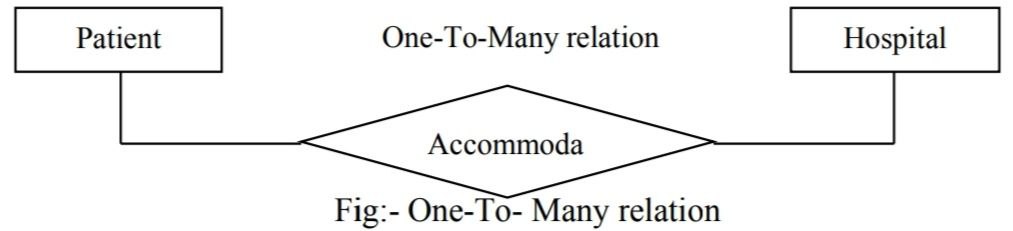
b.) One-To-Many
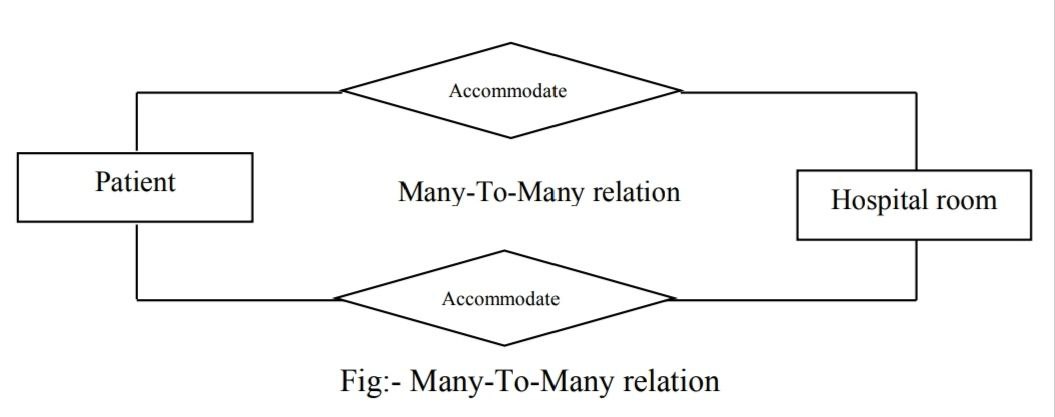
c.) Many-To-Many
Let us take the hospital environment to understand the relation types. The patient, bed, hospital room and surgeon are the entities in the environment and their relations are as shown below:
1. ERD for billing system
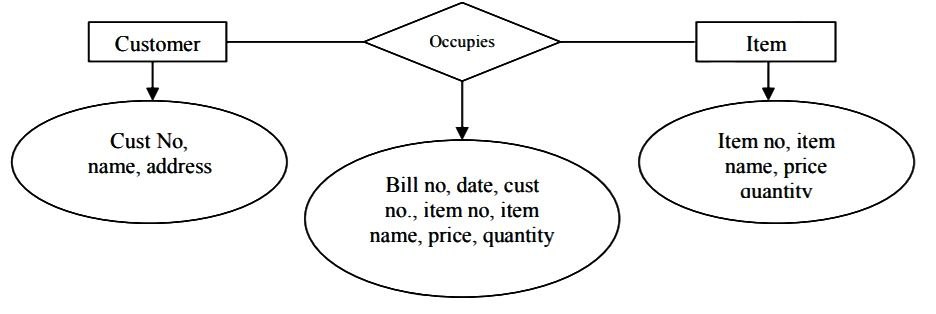
2. ERD for Car Driver
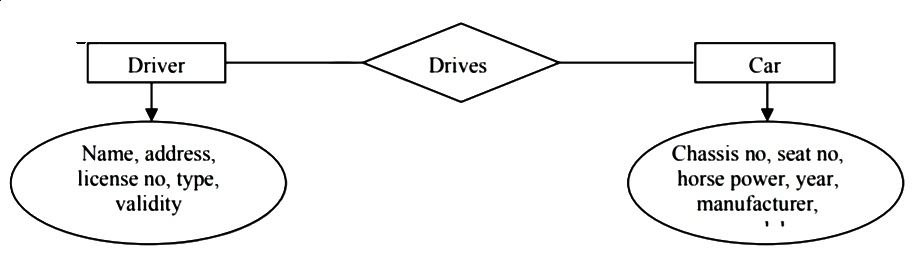
- Conceptually it is very simple.
- Better visual representation.
- Effective communication tool.
- Integrated with the relational database model.
- Easy conversion to any data model.
- Loss of information content.
- Limited relationship representation.
- No representation of data manipulation.
- Popular for high level design.
Structured Query Language, popularly known as SQL is the language that is designed for the retrieval and management of data stored in relational databased management system (RDBMS). It is called structured query language because it follows a rigorous set of rules and procedures in answering queries. It is also termed as 4GL. It allows an individual to create, update, delete, and retrieve data from database. SQL is simple and powerful query language that is capable of answering simple to most complex queries. It works along with database program such as DB2, Oracle, Informix, MS-Access, Sybase, MS SQL server etc.
Features of SQL:
- It is an English-like language. It uses words such as select, insert, delete as part of the command set.
- It is non-procedural language.
- It processes sets of records rather than a single record at a time. The most common form of a set of record is a table.
- It can be used by many users at a time.
- It provides command for creating, modifying, deleting, querying database objects.
- No coding is needed to manage the database system.
- No coding is needed to manage the database system.
- It is portable language.
- It is interactive type of language.
- It has multiple data views.
- It has complex interface.
- It is partially controlled by programmer.
- There are some SQL versions which have high operating cost.
Database design is a collection of processes that facilitate the designing, development, implementation and maintenance of enterprise data management systems. It helps to produce database systems; a) that meet the requirements of the users and b) have high performance.
Typical database design process are as follows:
i) Identify Entities: Everything that we want to put in a database is called entity. Some examples of entities are: Customers, Products, Shops, Sales etc.
ii) Identify Relationships: The next step is to determine the relationship between the entities and to determine the cardinality of each relationship.
iii) Identify Attributes: The data elements that we want to save for each entity are called attributes. For example, attributes of entity product are product name, manufacturer, price, manufacturer date, expiry date etc.
v) Draw ER Diagram: The ERD gives a graphical overview of the database.
v) Assign Keys: The next step is to define primary key (PK) and foreign key (FK) in the table. A PK is one or more data attributes that uniquely identify an entity. The FK is the reference to the primary key of another entity.
vi) Define the attribute's Data Type: Now it is time to figure out which data types need to be used for the attributes. Data can be Char, Integer etc.
vii) Normalization: Normalization makes data model flexible and reliable. Main goals of normalization are to reduce data redundancy and to remove data inconsistency. Different forms of normalization are: First Normal Form (1NF), Second Normal Form (2NF), Third Normal Form (3NF), Fourth Normal Form (4NF) and Fifth Normal Form (5NF).
Data Security or Database Security
The data security means protection from:
- Deliberate disclosure: The destroy of data by the unauthorized user by cracking the password and other security option deliberately is called deliberate disclosure. This may be happening from the competitors and working partner.
- Accidental disclosure: This may happen due to careless and by mistake by the smooth user or due to the accidents from fire, high voltage, mishandling of storage device and due to wrong connection of computer peripherals.
- Unauthorized alteration: The unauthorized access is possible by cracking password and other security break. This is done by hackers.
- Destruction:This is not the users hand but can perform some precautions on the system to avoid the destruction. Destruction due to fire, viruses, fluctuation of voltage and other natural disasters.
Points to Provide Security (Essential Steps to Secure Data)
- Establish Strong Passwords: The first step that every business must establish very strong passwords for all the accounts, bank details and other kinds of accounts that may not be easily guessed by anyone.
- Strong Firewall: We must establish a strong firewall in order to protect the network from unauthorized access or usage. The firewall protects the network by controlling internet traffic that comes into and goes out of our business.
- Antivirus Protection: Antivirus and antimalware solutions are also extremely important for data security and must be installed on systems. It helps us to fight with unwanted threats to our files and data.
- Secure Systems: Data loss can also be caused in case of laptop or mobile device is stolen. The easiest way to secure the system is to encrypt them. Encryption software help to make the information look coded so that no one who is unauthorized can view or access the data without a password.
- Backup Regularly: In order to avoid loss of data due to violation of data security, it is important to backup all the data regularly and keep it stored somewhere safe where it cannot be accessed or violated by anyone. One of the best way to backup the data is to either store it on hard disks or store it over cloud computing.
- Monitor Well: Another good practice that we must follow in order to secure our data is to monitor it well and diligently. We must always keep track of our data, know which data is stored where and use good monitoring tools that can help prevent data leakage.
- Surf Safely: Our data safety is in our hands, and if we are careful, there will be no way anyone would be able to violet it. Thus, it is important to be careful how we surf the net and what precautions we follow.
Data warehouse is a collection of data designed to support management decision making. It is a computer database that collects, integrates and stores an organization's data with the aim of producing accurate and timely management information and supporting data analysis. The primary goals of a data warehouse are the followings:
- Data consistency
- Provide access to the data of an organization.
- Capacity to separate and combine data
- Inclusion of tools set up query, analyze, and present information
- Publish used data
- Drive business re-engineering
The collection of data used by data warehouse may be characterized as:
- Subject Oriented: Data warehouse is oriented towards the major subject areas of organization which have been defined in data model. For example, an insurance company using a Data warehouse organizes their data by customer, premium and claim etc.
- Integrated: The data warehouse can receive data from a number of sources. Each of these sources had an application designer, each freely encoding, naming conventions, physical attributes and measurement of attributes. The filtering and translation necessary to transform many sources into one consistent database is known as integration.
- Non-volatile: Generally, in an operational environment data are frequently updated therefore changed, but same is not there in data warehouse because data are only loaded and accessed.
- Time variant: There is a connection between data and time when it was entered. The data warehouse contains a place for storing data that are five to ten years old or older, to be used for comparisons, trends, and forecasting.
- Banking Industry: Banking industry use data warehouse to analyze consumer data, market trends, government regulations and reports, and more importantly to help in financial decision making.
- Consumer Goods Industry: They use data warehouse for prediction of consumer trends, inventory management, market and advertisement research. In-depth analysis of sales and production is also carried out.
- Government: The government uses data warehouse to maintain and analyze tax records, health policy records and their respective providers, and also their entire criminal law database is connected to the state's data warehouse. Criminal activity is predicted from the patterns and trends, results of the analysis of historical data associated with past criminals.
- Education: Universities use warehouse for extracting of information used for the proposal of research grants, understanding their student demographics, and human resource management. The entire financial department of most universities depends on data warehouses.
- Healthcare: One of the most important sector which utilizes data warehouse is the Healthcare. All of their financial, clinical and employee records are fed to warehouses as it helps them to strategize and predict outcomes, track and analyze their service feedback, generate patient reports, share data with tie-in insurance companies medical aid services etc.
- Hospitality Industry: A major proportion of this industry is dominated by hotel and restaurant services, car rental services, and holiday home services. They utilize warehouse services to design and evaluate their advertising and promotion campaigns where they target customers based on their feedback and travel patterns.
- Insurance: The warehouse is primarily used to analyze data patterns and customer trends, apart from maintaining records of already existing participants.
- The Retailers: They use warehouse to track items, their advertising promotions, and the consumers buying trends. They also analyze sales to determine fast selling and slow selling product lines.
- Telecom Industry: The telecom industry operates over both offline and online data burdening them with a lot of historical data which has to be consolidated and integrated. Apart from those operations, analysis of fixed assets, analysis of customer's calling patterns for sales representatives to push advertising campaigns, and tracking of customer queries, all require the facilities of a data warehouse.
- More cost-effective decision making: A Data Warehouse allows reduction of staff and computer resources required to support queries and reports against operational and production databases. This typically offers significant savings.
- Enhanced business intelligence: The insight gained from data warehousing has a lot to do with improved access to information. Business leadership no longer has to make decisions based on incomplete information, so the decisions that affect strategy and operations are based on data-driven facts and supported by relevant information has gathered over time by the organizations. The increased business intelligence gain can be directly applied to business processes like market segmentation, inventory management, financial management and sales.
- Timely Access to Data: With data warehousing, users and business leadership have access to data from multiple sources as needed. This way, only a small amount of time is spent on the actual retrieval process.
- Enhanced customer service: An enterprise can maintain better customer relationships by correlating all customer data via a single Data Warehouse architecture.
- Business reengineering: In today's ever changing world, enterprises need to stay competitive and dynamic by means of re-engineering. Business re-engineering involves addressing changes, re-organizing, outsourcing, realigning etc. The data warehouse, leading to a process re-design that makes the business layer of an enterprise more effective.
- Information system engineering: Data warehouse development can be an effective first step in reengineering the enterprise’s legacy systems.
- Time Consuming: Before data can be stored within the warehouse, it must be cleaned, loaded, or extracted. This is a process that can take a long period of time.
- Maintenance costs outweigh the benefits: Data warehouses for a huge IT project would involve high maintenance systems which may affect the revenue for medium scale organizations.
- Data Ownership: An important concern of Data warehouses is security of data. Leaking of data within the same organization could lead to hiatus and cause problems for executives.
- Inability to capture required data: There is always the probability that the data which was required for analysis by the organizations was not integrated into the warehouse leading to loss of information.
- Increased demands of the users: After success with the initial few qureries, users of the facility may ask queries which would increase the workload on the system and server.
According to W. H. Inmon, who is known as father of the data warehouse gave the following major components of a data warehouse.
- Summarized Data: Summarized data is classified into two: Lightly summarized and Highly summarized. Lightly summarized data are the hallmark of a Data Warehouse. Highly summarized data are primarily for enterprise executions. Data volume at this is much less than other levels and represents and electric collection supporting a wide variety of needs and interests.
- Current Detail: The heart of Data Warehouse is its current detail, where the bulk of data resides. Current detail, organized by subject area, represents the entire enterprise, rather than a given application.
- 3. System of Record: A system of record is the source of the data that feeds the Data Warehouse. In other words, a system of record may be containing already summarized data.
- Integration and Transformation Program: As operational data items pass from their system of record to a Data Warehouse, integration and transformation programs convert them from application – specific data into enterprise data. These integration and transformation programs perform functions such as:
- Reformatting, recalculating or modifying key structures
- Adding time elements
- Identifying default values
- Supplying logic to choose between multiple data sources
- Summarizing tallying and merging data from multiple sources
- 5. Data warehouse architecture or Metadata: One of the most important parts of Data Warehouse is its metadata or data about data also called Data Warehouse architecture. Metadata that is used by Data Warehouse developers to manage and control Data Warehouse creation and maintenance resides outside the Data Warehouse.
- Archives: Data Warehouse archives contain old data (normally over two years old) of significant continuing interest and value to the enterprises. Archive data are most often used for forecasting and trend analysis. Archives include not only old data, they also include the metadata that describes the old data’s characteristics.
Data mining is defined as extracting information from huge sets of data. It is the process of selecting, exploring, and modelling large amounts of data to discover previously unknown relationships that can support decision making.Data mining software searches through large amounts of data for meaningful patterns of information. Data mining tools predict future trends and behaviors, allowing businesses to make proactive, knowledge-driven decisions. Data mining tools can answer business questions that traditionally were time consuming to resolve.
How does Data Mining Work? Or Stages in Data Mining
- Selection: Selecting or segmenting the data according to some criteria e.g. all those BCA students who have own a laptop, in this way subsets of the data can be determined.
- Preprocessing: This is the data cleansing stage where certain information is removed which is deemed unnecessary and may slow down queries for example unnecessary to note the sex of a patient when studying pregnancy.
- Transformation: The data is not merely transferred across but transformed in that overlays may added such as the demographic overlays commonly used in market research. The data is made useable and navigable.
- Data mining: This stage is concerned with the extraction of patterns from the data.
- Interpretation and evaluation: The patterns identified by the system are interpreted into knowledge which can then be used to support human decision making e.g. prediction and classification tasks, summarizing the contents of a database or explaining observed phenomena.
- Marking/Retailing::Data mining can aid direct marketers by providing them with useful and accurate trends about their customers’ purchasing behavior. Based on these trends, marketers can direct their marketing attentions to their customers with more precision. For example, marketers of a software company may advertise about their new software to consumers who have a lot of software purchasing history. In addition, data mining may also help marketers in predicting which products their customers may be interested in buying. Through this prediction, marketers can surprise their customers and make the customer’s shopping experience becomes a pleasant one
- Banking/Crediting: Data mining can assist financial institutions in areas such as credit reporting and loan information. For example, by examining previous customers with similar attributes, a bank can estimated the level of risk associated with each given loan.
- Law enforcement: Data mining can aid law enforcers in identifying criminal suspects as well as apprehending these criminals by examining trends in location, crime type, habit, and other patterns of behaviors.
- Researchers: Data mining can assist researchers by speeding up their data analyzing process; thus, allowing them more time to work on other projects.
- Governments: Data mining helps government agency by digging and analyzing records of the financial transaction to build patterns that can detect money laundering or criminal activities.
- Education: Data Mining techniques can be applied in educational environment to analyze student learning behavior, performance during academic year, and even prediction on how the student will perform during an exam.
- Fraud Detection: Another relevant field of application, fraud detection affects different industries such as banking (credit card fraud detection, illegal transactions) and insurance (checking for false claims).
- Web Mining: Web Mining applications are made to analyze clickstreams – the sequence of visit from users in websites. It is useful in analyzing e-commerce websites, as it can offer customizes pages for customers.
- Text Mining: Text Mining attempts to gather meaningful information from different kind of texts, in order to classify documents, books, e-mail and web pages. An example of text mining application includes creation of filters for e-mail messages and newsgroup.
- Future Healthcare: Data mining holds great potential to improve health systems. It uses data and analytics to identify best practices that improve care and reduce costs. Mining can be used to predict the volume of patients in every category. Processes are developed that make sure that the patients receive appropriate care at the right place and at the right time.
- Privacy Issues: Personal privacy has always been a major concern in this country. In recent years, with the widespread use of Internet, the concerns about privacy have increased tremendously. Because of the privacy issues, some people do not shop on Internet. They are afraid that somebody may have access to their personal information and then use that information in an unethical way; thus causing them harm.
- Security issues: Although companies have a lot of personal information about us available online, they do not have sufficient security systems in place to protect that information. For example, recently the Ford Motor credit company had to inform 13,000 of the consumers that their personal information including Social Security number, address, account number and payment history were accessed by hackers who broke into a database belonging to the Experian credit reporting agency. This incidence illustrated that companies are willing to disclose and share your personal information, but they are not taking care of the information properly. With so much personal information available, identity theft could become a real problem.
- Misuse of information/inaccurate information: Trends obtain through data mining intended to be used for marketing purpose or for some other ethical purposes, may be misused. Unethical businesses or people may use the information obtained through data mining to take advantage of vulnerable people or discriminated against a certain group of people.
A database administrator is the individual responsible for maintaining the RDBMS system. The DBA has many different responsibilities, but the overall goal of the DBA is to keep the server up at all times and to provide users with access to the required information when they need it. The DBA makes sure that the database is protected and that any chance of data loss is minimized. A DBA needs the following:
- Knowledge of the operating system in which database server is running.
- Knowledge of Structured Query Language (SQL)
- Sound database design
- General understanding of network architecture (e.g. Client/Server, Internet/Intranet, Enterprises etc.)
- Knowledge about the database server
The advances in computer and its architecture have also resulted in the advances in databases and its architecture have also resulted in the advances in databases and its architecture.
- Centralized Database Architecture A centralized database holds all of an organization's data on a central computer such as a mainframe computer or server. Users in the organization can access the data from their own PC or terminal.
The advantages of the database being centralized- Easier to organize, edit, update and back-up the data
- Less data duplication - data is only entered once but can be accessed by many users
- Data integrity - because data is stored once different data is no longer held in different databases in various departments around the organization.
Client-Server systems involve a client machine and a server machine. A computing paradigm based on client server architecture makes it possible to inter operate among different database management systems, among a network of heterogeneous hardware and software platform. Here the load is optimally distributed among clients and servers. Servers, in general, are high performance machines that support heavy transaction processing known as server processes, whereas the clients are low-end microcomputers with rich graphical user interface (GUI). With client server architecture, a network user can initiate several client processes in many windows among many servers; they could be heterogeneous hardware and software running on machines that are geographically dispersed. The client is connected to the server via a communication link. The client interacts with the server when it requires access to any additional functionality that does not exist in its own machine. Client provides interfaces to access and utilize the server resources. The DBMS architecture on the Client-Server systems are of two kinds- two-tier Client-Server architecture and three tier Client-Server architecture.
- Two-tier Client-Server Architecture: In this architecture the user interface programs and the application programs run on the client side. An Application Program Interface (API) allows client side programs, to call the DBMS which is at the server side. The client programs use Open Data Base Connectivity (ODBC) or Java Data Base Connectivity (JDBC) interfaces to communicate with the database.
- Three-tier Client-Server Architecture: In this architecture, In addition to the client and the database servers, it has an intermediate layer or middleware called Application Server or Web Server. The web server stores the application or business logic part of the application. The client stores the user interface. The DBMS is stored at the server side. The web server acts like a pipe for receiving the client request, processing it and accessing the data from the DBMS server, and sending it back to the client.
A distributed database, as the name indicates, is stored in more than one physical location. The database is stored partly in one location while it is partly stored and maintained in other locations. In other words, a distributed database coordinates data access from various locations; however, all the components are logically related.. In this approach, databases are designed as an entity and are linked through communication networks. This approach is alternative to the central database approach. Nowadays, many databases are distributed across geographical areas. For example, networks of libraries, networks of banks, network of offices of organizations across the world etc.
(Click Here to Download This Note)
CFA Chapterwise
