Home / First Semester
Chapter 3: Operating Systems
Contents:
Introduction, Functions and Types of Operating System, Open Source Operating System, Memory Management, Deadlock, Memory Fragmentation Virtual Memory and Linux
An operating system (OS) is a large collection of system software, which manages the resources of computer system such as memory, storage, processor, I/O devices. It also acts as an interface between machine and user. It is an organized set or collection of software that controls the overall operation of the computer system and provides an environment where the user can execute the programs in a convenient and efficient manner. Examples are: MS-DOS, Windows, Linux, Unix, MacOS etc.
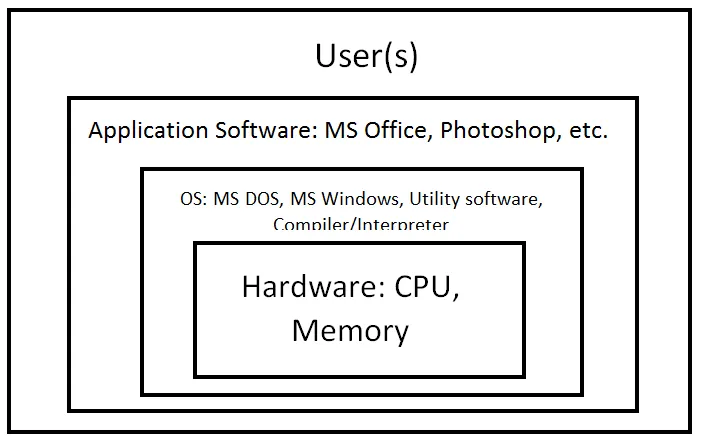
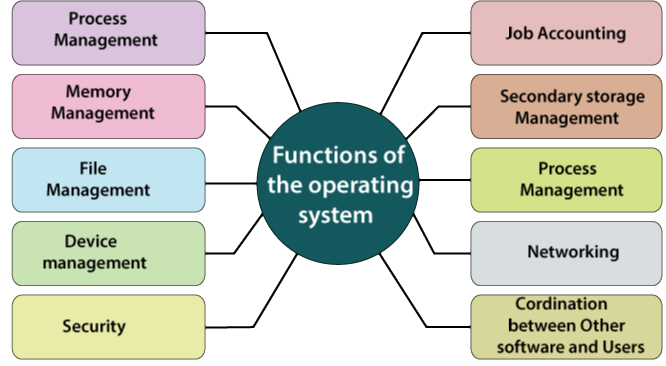
The main function of the operating system includes:
- Operating CPU of the computer.
- Controlling Input/ Output devices that provide an interface between the user and the computer.
- Handling the working of application programs with the hardware and other software systems.
- Managing the storage and retrieval of information using storage devices such as disks.
1. Process Management:
In multiprogramming environment, more than one program resides in memory at the same time. A set of instructions stored in secondary storage device is called program. When a program is loaded into memory, it will be ready for execution and is termed as process. Simply, we can say that a program in action is called process. All these processes compete for CPU and some other shared resources, and also need to communicate with each other. OS does the following activities for process management.
- Process scheduling
- Keeps status of processes
- Inter-process communication
When multiple processes are running, some processes may demand the input/output devices. In such case the process goes to the blocked state until the device is available. When concurrent processes are under execution, the CPU time is given to a single process at a time. The process which gets the CPU time is in the running state. The process which is waiting for CPU time is in the ready state.
2. Memory Management:
It refers to management of primary memory or main memory. All the programs are loaded in the main memory before their execution. It is the function of the operating system to determine how much memory should be provided to each process. The activities of memory management handled by operating system are:-
- Allocate memory
- Free memory,
- Re-allocate memory to a program when a used block is freed and,
- Keep track of memory usage.
The OS manages the files and directories of a computer system. A file can be defined as a collection of information or data that is stored in the memory of a computer system. Every file has a unique name associated with it. The organization of files and directories in a computer system is referred as file system. File management describes the fundamental methods for:
- Naming files
- Defining file structure
- Defining file access methods
- Defining file attributes and operations
- Storing and handling files
This function of operating system deals with the management of peripheral devices such as printer, mouse and keyboard attached to a computer system. An operating system interacts with the hardware devices through specific device drivers. The device management tasks handled by operating system are:
- Open, close and write device drivers, and
- Communicate, control and monitor the device driver.
Operating system is responsible for providing proper authentication and authorization to computer system and its resources. Authentication is the process of verifying identity of users before allowing to use computer system and its resources. Normally authentication is provided by means of passwords. On the other hand, authorization is the process of providing access rights or privileges for objects to users.
6. User Interface or Command Interpreter:
OS provides an interface between the computer user and the computer hardware. The user interface is a set of commands or a graphical user interface via which the user interacts with the applications and the hardware.
Types of Operating System
Based on the capabilities and the types of application supported, the operating system can be divided into six major categories:
Based on Processing Method
1. Batch Processing OS:
A batch is group of similar types of jobs which are stored in secondary storage especially magnetic tape. It is not a complete operating system. It is traditional way of data processing mechanism, specially used in mainframe computer early day of computing. In this system, jobs (combination of data and program) are grouped together and processed one after another. So, next job gets chance to be executed only after the completion of current job. Batch processing OS carried out from beginning to end without user intervention. It takes long computation time. For example, weather forecasting, statistical analysis etc.
2. Multiprogramming OS:
To overcome the problem of under utilization of CPU and main memory, the multi-programming was introduced. The multi-programming is interleaved execution of multiple jobs by the same computer.
In multi-programming system, when one program is waiting for I/O transfer; there is another program ready to utilize the CPU. So it is possible for several jobs to share the time of the CPU. But it is important to note that multi-programming is not defined to be the execution of jobs at the same instance of time. Rather it does mean that there are a number of jobs available to the CPU (placed in main memory) and a portion of one is executed then a segment of another and so on. A simple process of multi-programming is shown in figure:
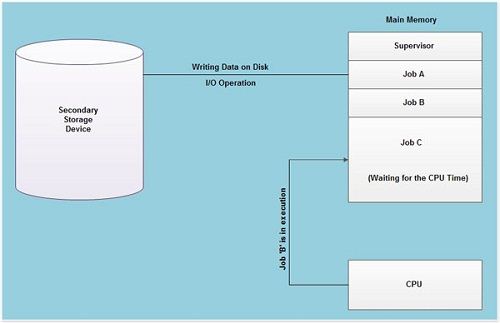
Multi-programming is a common approach to resource management. The essential components of a single-user operating system include a command processor, an input/ output control system, a file system, and a transient area. A multi-programming operating system builds on this base, subdividing the transient area to hold several independent programs and adding resource management routines to the operating system’s basic functions.
3. Multitasking OS:
Multitasking operating system provides the interface for executing the multiple program tasks by single user at a same time on the one computer system. In multitasking, only one CPU is involved, but it switches from one program to another so quickly that it gives the appearance of executing all of the programs at the same time. In the modern operating systems, we are able to play MP3 music, edit documents in Microsoft Word, surf the Google Chrome all simultaneously, this is accomplished by means of multi tasking.
There are two basic types of multitasking:
- Pre-emptive: In pre-emptive multitasking, the OS allows CPU time slices to each program OS/2, Windows NT and Unix use pre-emptive multitasking.
- Non-pre-emptive: In non-pre-emptive multitasking, each program can control the CPU for as long as it needs. If a program is not using the CPU, however, it can allow another program to use it temporarily. It is also called cooperative multitasking. Microsoft Windows 3.x and above, MacOS use cooperative multitasking.
Multiprocessing is a processing done by two or more processors linked together to perform work simultaneously and precisely at the same time. Processing takes place in parallel and is also called parallel processing. Each processor works on different parts of the same task, or, on two or more different tasks. Since execution takes place in parallel, they are used for high-speed execution, and to increase the power of computer. Linux, Unix, Windows and MacOS are examples of multiprocessing OS.
5. Real Time OS:
The real time operating system has well defined; fixed time constraint and processing must be done within fixed time constraint. This OS provides quick response time.
The real-time operating system used for a real-time application means for those applications where data processing should be done in the fixed and small quantum of time. It is different from general purpose computer where time concept is not considered as much crucial as in Real-Time Operating System.
Real time Operating Systems are very fast and quick respondent systems. These systems are used in an environment where a large number of events (generally external) must be accepted and processed in a short time. Real time processing requires quick transaction and characterized by supplying immediate response. For example, a measurement from a petroleum refinery indicating that temperature is getting too high and might demand for immediate attention to avoid an explosion.
Few more examples of real time processing are:
- Rocket launching system
- Monitoring and controlling nuclear power station
- Traffic light control
- Airline’s reservation system
- Air traffic control system.
- Systems that provide immediate updating.
- Systems that provide up to the minute information on stock prices.
- Defense application systems like as RADAR
- Hard real time OS: A process should be executed in given deadline. The deadline should not be crossed. Preemption time for Hard Real-Time Operating System is almost less than few microseconds. Examples are Airbag control in cars, anti-lock brake, engine control system, etc.
- Soft real time OS: A process might not be executed in given deadline. It can be crossed it then executed next, without harming the system. Example are a digital camera, mobile phones, etc.
Time-Sharing Operating Systems is one of the important types of operating system. Time-sharing enables many people, located at various terminals, to use a particular computer system at the same time. Multitasking or Time-Sharing Systems is a logical extension of multiprogramming. Processor’s time is shared among multiple users simultaneously is termed as time-sharing.
An operating system uses CPU scheduling and multiprogramming to provide each user with a small portion of a time. Computer systems which were designed primarily as batch systems have been modified to time sharing systems.
7. Network OS:
Network Operating System is an operating system that includes special functions for connecting computers and devices into a local-area network (LAN) or Inter-network. Short form of Network Operating system is NOS. Some popular network operating systems are Windows, Linux, MacOS etc. The network operating system which was first developed is Novell Netware. It was developed in 1983.
An operating system that provides the connectivity among a number of autonomous computers is called a network operating system. A typical configuration for a network operating system is a collection of personal computers along with a common printer, server and file server for archival storage, all tied together by a local network.
Based on User Interface
1. Graphical User Interface (GUI):
The concept of GUI is invented by Xeros Corporation in 1970, but it is used in business by Apple Corporation in first time in 1983 and Macintosh computer introduced its updated form in 1984. The Microsoft has launched operating system with GUI, after Apple.
GUI allows us to enter commands by pointing and clicking at objects that appears on the screen. The main advantage of GUI is that it is easy to use. The disadvantage of GUI is the amount of memory space they need. It needs a lot of RAM and hard disk space to run.
Features of GUI:
- It is graphical and user friendly.
- Users don’t have to remember syntax and commands.
- It needs large amount of memory space.
- It needs faster processor to operate.
- Other peripherals like mouse, light pen, joystick etc. can be used.
- GUI based OS are usually 32-bit or 64-bit operating system.
- It supports multimedia environment.
- It supports multitasking, multiprogramming, multithreading etc.
Command-Line-Interface (CLI)/Text Based Interface (TBI)/Character User Interface (CUI), where the user provides the input by typing a command string with the computer keyboard and the system provide output by a printing text on the computer monitor. The main advantage of CUI is that they can be quick to use. Since, there are no involvements of graphical components, so CUI requires less memory to operate it. The disadvantage of CUI is that they are very difficult to use if the user doesn’t know the correct commands. DOS is very commonly used example of CUI.
Features of CUI:
- It is more textual and less user friendly.
- Users have to remember syntax and commands.
- It needs less amount of memory space.
- It doesn’t contain different components such as text box, icon, desktop, pointing devices etc.
- It is faster in compare to GUI
- Other peripherals like mouse, light pen, and joystick are not recognized.
- It cannot display graphics, pictures or icons.
- CUI based OS are usually 8-bit or 16-bit operating system.
- It does not support multimedia environment.
- It does not support multitasking, multiprogramming, multithreading etc.
1. Single User OS:
Single-user OS allows one user at a time. Normally, one user program is only allowing to be run and processed at a time. So, there is no multiprogramming of user programs. It is based on small microcomputer which allows a single user to operate the machine. Examples are MS-DOS, PC-DOS etc.
2. Multi User OS:
Multi-user OS allows two or more users to run program at the same time. Some operating systems permit hundreds or even thousands of concurrent users. The operating systems of mainframes and minicomputers are multi-user systems. Examples are: Unix, Linux, Windows, MacOS etc.
Open-Source Operating System
Open source refers to a program or software in which the source code (The program written by programmer) is available to the general public for use and / or modification from its original design free of charge. Software that are available free of cost are called free software and the software whose source code is known publicly is called open-source software. Open-source software is always free software.
Open-Source Operating System is any operating system that is free to use, modify/enhance the operating system, and redistribute the modified (or unmodified) form of the operating system. The advance user can modify the code of the operating system to make it works better for them in starting the computer or likely user interface.
Open-Source operating systems are released under a license where the copyright holder allows others to study, change as well as distribute the software to other people. The different open-source operating systems are available in the market are: Linux, Unix, Ubuntu, Cosmos, FreeDOS, Genode, Ghost OS, ITS, OSv, PhantomOS etc.
Memory Management
Memory management is the functionality of an operating system which handles or manages primary memory and moves processes back and forth between main memory and disk during execution. Memory management keeps track of each and every memory location, regardless of either it is allocated to some process or it is free.
Deadlock:
A deadlock in OS is a situation in which more than one process is blocked because it is holding a resource and also requires some resource that is acquired by some other process. The four necessary conditions for a deadlock situation to occur are mutual exclusion, hold and wait, no preemption and circular set.
Memory fragmentation
Fragmentation is an unwanted problem in the operating system in which the processes are loaded and unloaded from memory, and free memory space is fragmented. Processes can't be assigned to memory blocks due to their small size, and the memory blocks stay unused. The problem of internal fragmentation may arise due to the fixed sizes of the memory blocks. It may be solved by assigning space to the process via dynamic partitioning. Dynamic partitioning allocates only the amount of space requested by the process.
Virtual memory
Virtual memory is a common technique used in a computer's operating system (OS). Virtual memory uses both hardware and software to enable a computer to compensate for physical memory shortages, temporarily transferring data from random access memory (RAM) to disk storage.
Linux
It is an open-source powerful UNIX based OS which runs on varieties of platforms including Intel, SPARCE and Power PC. It is a multi-user, multi-tasking, multi-programming operating system mainly popular for server OS. It is distributed through different distributors such as Red Hat, Mandrate, Open Suse, Ubuntu, Slackware, Sobayon, Debian, Mandriva, Fedora, Genten, Granular Linux.
(Click Here to Download This Note)
CFA Chapterwise
