Home / First Semester
Chapter 1: Introduction to Computer System
Computer architecture refers to the definitions of basic attributes of hardware components and their interconnections, in order to achieve certain specified goals in terms of functions and performance. In other words, the design, arrangement, construction or organization of the different parts of a computer system is known as computer architecture. It is the conceptual design and fundamental operational structure of a computer system.
There are basically two types of digital computer architecture. The first one is called Von Neumann architecture and later Harvard architecture was adopted for designing digital computers.
1. Von Neumann Architecture
It is named after the mathematician and early computer scientist John Von Neumann. According to this architecture, computers have single memory that stores both program and data. Every computer has processing unit containing an arithmetic logic unit (ALU), processor registers and a control unit. In this architecture an instruction fetch and a data fetch cannot occur at the same time because they share a common bus.
2. Harvard Architecture
The name originated from an old computer "Harvard Mark I". In this architecture computers have two separate memories for storing data and programs. Most of the modern computer architectures are based on Harvard architecture. Thus it is possible to access program memory and data memory simultaneously. Typically, program memory is read-only and data memory is read-write. Therefore, it is impossible for program contents to be modified by the program itself.
Anatomy of Digital Computers
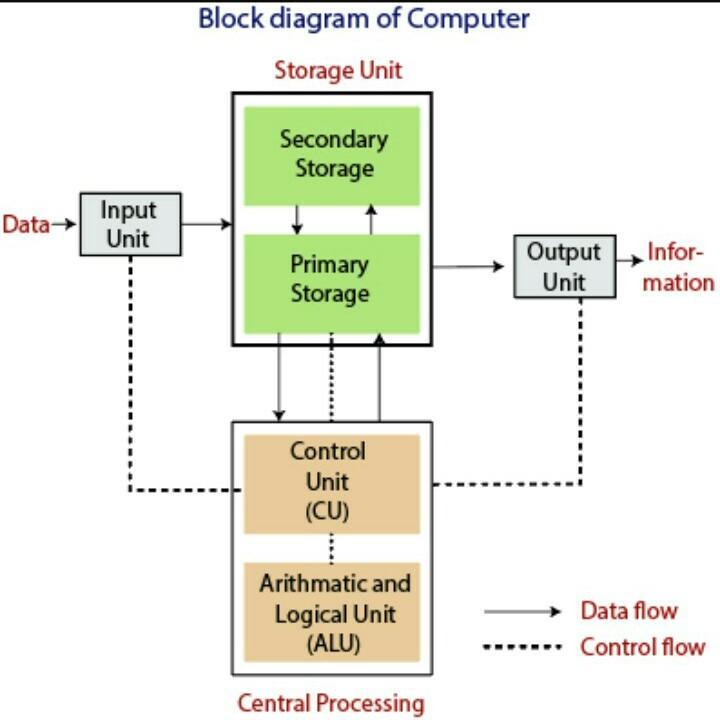
A computer contains different hardware components that interact with each other to perform the task. Major hardware components in computer systems are: Input Unit, Output Unit, Processor and Storage. Relationship between these components is shown in above figure:
Input Unit: It accepts data or instructions given by the user and it converts the data and instructions from man readable to machine readable code. Some common input devices are keyboard, mouse, scanner, touch screen, light pen etc. Output Unit: It provides the result after processing the data to the users. It converts the output into the user understandable format before providing it to the users. Some common output devices are: monitor, printer, speaker, plotter etc.
Processor/Central Processing Unit: The part of the computer that executes program instructions is known as processor or central processing unit (CPU). The central processing unit carries out each instruction program in sequence, to perform the basic arithmetical, logical, and input/output operation of the system. A CPU built on a single chip is called a microprocessor. It consists of three components. They are: Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), Control Unit (CU) and Registers.
Storage/Memory: It is responsible for storing data and instructions either for short or longer period of time. Memory devices are of two types:
1. Primary or Main memory: It is the main memory of the computer. It is used for storing data and instructions during processing. It is the only memory which is directly accessible to the CPU. It is usually expensive, faster for read/write operation and used in small storage capacity. Examples are: RAM, ROM, Cache Memory.
2. Secondary or auxiliary memory: It is the additional memory of the computer. It is used for storing huge amount of data for longer period of time. It is also used for transferring data from one computer to another. It is usually cheaper, slower, and used in larger storage capacity. It is not directly accessible to the CPU; it requires primary memory for its operations. Examples are: Hard disk, CD, DVD, Pen drive etc.
Bus Architecture
In computer architecture, a bus is a collection of wires, chips and slots inside the computer through which data is transmitted from one part or component of the computer to another, to and from peripherals devices. Each component of the computer is connected to these buses.
The functions of bus are:
- It carries information from one computer to another.
- It carries data, address or control signal.
- One component of the computer can interact with others through the bus.
- Address Bus
- Data Bus
- Control Bus
Address bus is used to specify the address of the memory location to be accessed. CPU reads data or instructions from memory locations by specifying the address of its location and CPU writes data to the memory locations by specifying the memory address. Address bus is unidirectional. This means, the address bus carries memory location in only one direction, from CPU to memory, both for read and write operation.
ii) Data Bus:
Actual data is transferred via the data bus. In case of read operations, the CPU sends an address to memory; the memory will send data via the data bus in return to the CPU. In case of write operation, CPU sends an address via address bus and data via data bus. The data bus is a bidirectional bus, meaning the data can be transferred from CPU to main memory and vice versa.
iii) Control Bus:
It is the path for sending the control signals generated by the Control Unit. Data and Address bus is shared by all the components of the system through the control bus. Some control signals are: Read, Write and Fetch etc. Control bus is used to tell what to do with the selected memory location. Various operations are performed by microprocessor with the help of a control bus. If the CPU needs to perform write operation on memory it sends 'write' signal via control bus but if CPU needs to perform read operation on the memory 'read' signal is sent via the control bus. Control bus is also unidirectional because only the CPU sends control signals to other devices.
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The CPU is like the brain of a computer that organizes and executes instruction. Its primary function is to execute instruction. Besides executing instructions, the CPU controls the operation of all other components such as memory, input and output devices. Under its control, programs and data are stored in memory, displayed on the monitor or printed on the paper. A CPU built on a single chip is called a microprocessor. Nowadays, microprocessors are also called processors.
The functions of the CPU (Processor) are:
- To carry out processing.
- To give commands to all parts of the computer system.
- To control the sequence of operations.
- To control the storage of data or instructions.
- To perform arithmetic and logical calculations.
- Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU)
- Control Unit
- Register Array
The main operations are summarized below:
- It performs basic arithmetical calculations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, division etc.
- It performs logical operations such as comparing greater than, equal to etc.
Functions of the Control Unit:
- The CU carries out the controlling operations of computers.
- It performs data processing operations.
- It sends control signals to various parts of the computer system for controlling.
- It gives commands to input data from input unit to memory unit to ALU.
- It transforms results from ALU to memory unit to output unit.
- It gives commands to store the data, instruction and program in memory.
Features of Register:
- They are the fastest memory of computer.
- The storage capacity of the register is small.
- They are temporary memories of computers.
Storage or Memory Unit
Memory unit is responsible for storing data and instructions either for a short or longer period of time. Memory device of two types:
a) Primary Memory or Storage: It is also known as system memory or main memory or primary storage or internal memory of the computer. It is used for storing data and instructions during processing. It is the working area for the computer's processor. It is the only memory which is directly accessible to CPU. As soon as a computer starts, primary memory stores all running applications, operating system (OS), user interface and any others.
It has three tasks:
Features of Primary Memory:
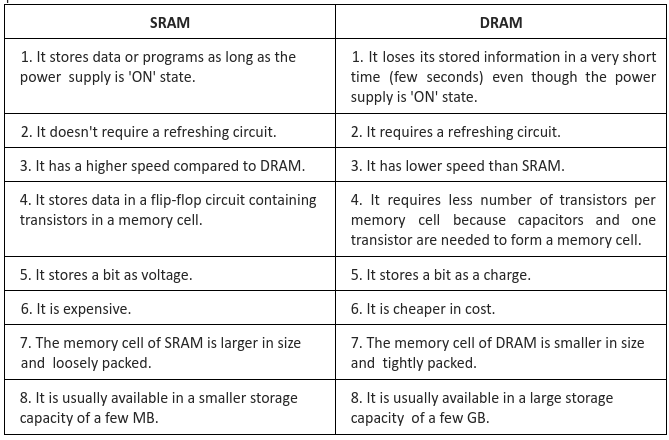
RAM is the read/write memory of the computer. It is the memory that holds instructions and data that are used frequently during processing. It is referred to as random access memory because it is possible to randomly select any location of the memory to store and retrieve data. It is volatile memory i.e. it stores data or information as long as the power supply is on, when the power supply goes off, the stored content in the RAM will be lost.
RAM is used to store:
There are two types of RAM:
2. Dynamic Random Access Memory (DRAM): In DRAM, the stored data will be lost after a few milliseconds even if the computer is ON state. So, to prevent data loss, a refreshing circuit is required. It is cheaper but slower for read/write than SRAM. It stores data in the form of charge. It is popularly at present.
ii) Read Only Memory (ROM):
It is the primary memory that stores some standard processing programs supplied by the manufacturers to operate the personal computer. The CPU can only read the content of ROM but it cannot change the content of ROM. The basic input/output program is stored in the ROM that examines and initializes various equipment attached to the PC when the switch is made ON. It is non-volatile memory because it doesn't lose its content on failure of power supply.
Types of ROM:
Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EPROM): EPROM is an erasable PROM. The data stored in EPROM can be erased by exposing it to strong ultraviolet (UV) light. When an EPROM is exposed to ultraviolet light, the entire data are erased. It is usually reprogrammed without removing it from the circuit board.
C) EEPROM (Electrical Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory): EEPROM is an electrically erasable PROM. It can be erased and reprogrammed on the byte by byte basis. Either a single byte or the entire chip can be erased in one operation. It requires much shorter time, a few milliseconds for erasing as compared to EPROM. It need not be removed from the circuit board for erasing as EPROM. EEPROM is similar to flash memory (sometimes called flash EEPROM). The principle difference is that EEPROM requires data to be written or erased one byte at a time whereas flash memory allows data to be written or erased in blocks. This makes flash memory faster.
iii) Cache Memory
It is extremely fast memory that is built into a computer's CPU or located next to it on a separate chip. The speed of the CPU is extremely high compared to the access time of the main memory. Therefore, the performance of the CPU decreases due to the slow speed of main memory. To overcome such a problem, a small memory chip is attached between CPU and main memory whose access time is very close to the processing speed of the CPU. It is called cache memory. It is used to store instructions and data frequently used by the CPU from RAM.
If the CPU needs data first of all it searches the cache memory for the data. If data is found in cache it is called cache hit and data is sent to the CPU. But if data is not found in cache, it is called cache miss. In case of cache miss, search request for data goes to RAM and the data is sent to CPU as well as one copy of the data is stored in cache so that the data can be found in cache for future references. Therefore, cache memory only stores a copy of data that is present in RAM. It is actually static RAM.
Cache can be further classified into two categories:
Level 1 Cache (L1): It is also called primary or internal cache. It is built directly into the processor chip. It is the smallest, fastest and most expensive cache memory. CPU looks to L1 cache first for data.
Level 2 Cache (L2): It is slower than L1 cache. Its storage capacity is more and it is also less expensive than L1. This cache is separate from the processor chip on the motherboard.
b) Secondary memory or Storage Devices:
Secondary memory is non-volatile memory i.e. stored data and instructions retained even if the power supply is cut off. It is also called auxiliary memory or backup memory. It is used primarily to store large volumes of data on a permanent basis that can be partially transferred to primary storage, whenever required for processing. Comparatively, secondary memory is cheaper than the main memory according to per bit cost.
Features of Secondary Memory:
The modern computer uses the following types of memory
1. Magnetic Disk or Memory
It is the most common secondary storage device in a computer system. Generally, it is a random access device. It contains circular disks, which are made of metal (aluminum) or a thin plastic (Mylar) coated with iron oxide on both sides. It allows the recording of data in the form of magnetized spots. The data are stored on the disks in a number of concentric circles called tracks. Tracks are divided into sectors. All the tracks have the same number of sectors. The most common magnetic disks are floppy disk and hard disk.
Advantages
Hard disk
Hard disk is a magnetic disk that is used as secondary memory for mass storage of data permanently. It stores programs, data, operating system, compilers, assembler, application program, and database. A single hard disk usually consists of several platters. Each platter requires two read/write heads, one for each side. All the read/write heads are attached to a single access arm so that they can move independently. It is generally made up of aluminum and is coated on both sides with the special iron oxide to store data in the form of magnetized spots. The platter is mounted on a stack on a spindle driven by the motor connected to the spindle. It rotates at very high speed between 3600 rpm to 15000 rpm (revolution per minute) or more. The average access time is about 15ms.
Floppy disk
A floppy disk, also known as diskette, is a removable round, flat piece of Mylar plastic, that stores data and programs as magnetized spots. It is used to move files between different computers, load new programs onto the computer, or store backup of data and small programs. It is not very reliable and can be damaged easily. Floppy comes in two basic sizes: 5.25 inch, which can hold 1.2 MB of data and 3.5 inch, which can hold 1.44 MB of data.
Flash Memory
It is used in small portable computers. Flash memory or flash RAM cards, consists of circuitry on credit card-size cards that can be inserted into slots connecting to the motherboard. Unlike standard RAM chips, flash memory is nonvolatile. Flash memory can be used not only to simulate main memory but also to supplement or replace hard disk drives for permanent storage.
b) Optical Disk
It is a removable disk on which data is written and read through the use of laser beams. A laser beam is a concentrated narrow beam of light, focused and directed on a particular location to read or write data. It is used as backup memory.
Advantages
There are three types of optical disks:
- Compact Disk (CD)
- DVD (Digital Versatile Disk)
- BD (Blu-Ray Disk)
It is a data storage format, which basically means that it is used to store data. It is portable and its capacity usually ranges from 650 to 750 MB. There are three basic types of compact disk(CD).
i) CD-ROM (Compact Disk Read Only Memory): It stands for CD-Read Only memory. It is written during the process of manufacturing by high power laser beam. The data is permanent and can be read any number of times, but CD-ROMs cannot be modified.
ii) CD-R (Compact Disk Recordable): It stands for CD-Recordable. It is a CD format that allows you to write data onto a specially manufactured disk, which can then be read by a standard CD-ROM drive. It is once writable CD, i.e. the change of state is permanent, so it is also called WORM (Write Once Read Many) media.
iii) CD-RW (Compact Disk Rewritable): It can be reused by erasing the content of the CD and again writing data on it. Using, CD-RW drive, user can write data onto special re-writable compact disk, then over write it with new data. It has the same capacity as standard compact disk, and most can be over written up to 100 times.
b) Digital Versatile Disk (DVD)
It is primarily used to store movies or music. However, it can hold any type of information. It is similar to a CD but has larger storage capacity as much up to 4.7 GB on one disc. Like CD, DVD also have three types DVD-ROM, DVD-R, DVD-RW.
C) Blu-Ray Disk (BD)
It is the name of the new generation optical disk. It is developed to enable recording, rewriting and play back of high definition video (HD), as well as storing large amount of data. It can hold up to 25 GB on a single layered disk and 50 GB on a dual layered disk. The current optical disk technology such as DVD uses red laser to read and write data, the new disk, BD uses blue-violet laser beam, hence the name Blu-ray used. Similar to CD and DVD, it also has different variations. Such as BD-ROM, BD-R and BD-RW.
CFA Chapterwise
